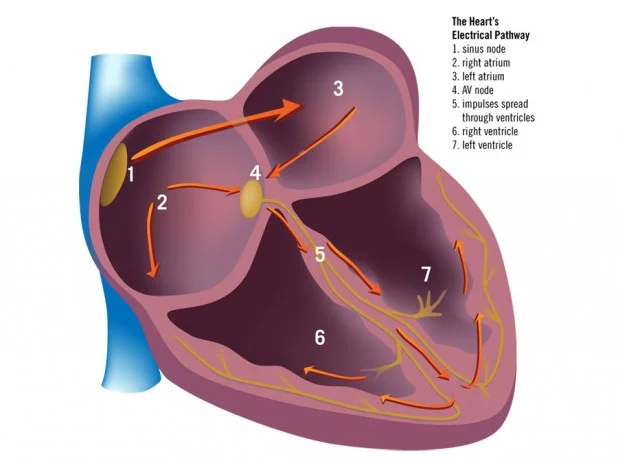
The healing process has begun. Going home is a welcoming thought, but fears and concerns can accompany it. This is normal. After all, you were monitored closely for several days at the hospital and now you will be managing on your own. Your goals for the first two weeks are to follow the going home instructions, walk daily as prescribed and relax. Remember, your body is adjusting to a new health condition and to new medications that may make you feel more tired than usual.
Sit down, put your feet up and take a nap if you are tired. Listen to your body. This is the time to let others help you. Do activities that are easy and enjoyable such as playing games, watching movies, reading and just talking.
Most people do not return to work until after they have a follow-up visit with the doctor and start a cardiac rehabilitation program. Use your progressive walking program (see bottom of page) to guide you with your daily walking and refer to the “Exercising for a Healthier Heart” section in this binder for further guidelines. Remember, this lower level of activity is temporary.
It is common for you (and your partner) to feel a wide range of emotions after experiencing a heart attack. Limiting your activities, being out of your normal routine and becoming bored can affect the way you feel. At times, you may find yourself feeling tearful and depressed or you may feel overwhelmed with thankfulness and gratitude. Other common feelings are anger with yourself and those closest to you, discouragement when you don’t think you are improving as fast as you should or just being quietly scared that it will happen again. Express your feelings. Sharing with others can make the road to recovery a lot less bumpy.
Returning to sexual activity may be a concern of yours. You may not feel any desire for sexual activity at first, or you may worry it will trigger another heart attack. Actually, your risk for another heart attack during sex is low. Ask your doctor when you can return to sexual activity. In most cases, you can resume when you are able to climb two flights of stairs without chest pain, shortness of breath or an irregular heart rate. Meanwhile, showing affection with hugs, caresses and kisses is a good way to get back in touch with your partner.
Having a heart attack is a life-changing event. It is a time to become aware of what risk factors caused the problem and to make appropriate lifestyle changes (see section on “Lifestyle Changes for a Healthier Heart”).
Your doctors and a cardiac rehabilitation program will guide you on this new journey to wellness.